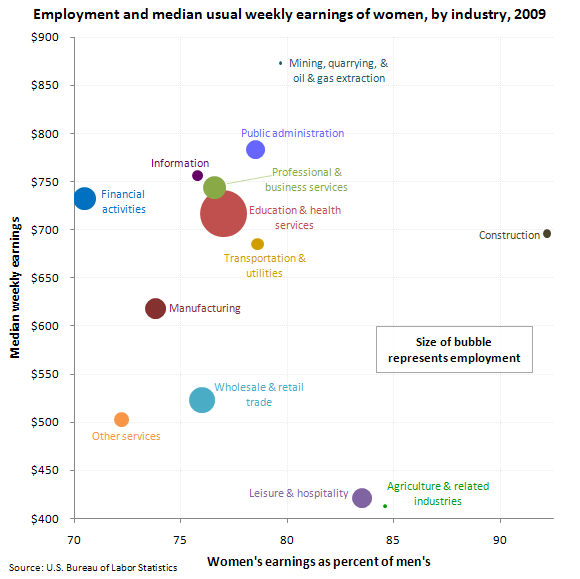
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Highlights of Women’s Earnings in 2009.“ Data refer to the sole or principal job of full- and part-time workers, for wage and salary workers.
The Assessment Committee gathers, reviews, and synthesizes data on the status of women; interprets this data to identify gender-based inequities; and recommends solutions. The committee also compiles periodic reports on the status of women at the University and provides consultation to other Commission for Women committees seeking data relevant to their studies.

Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, “Highlights of Women’s Earnings in 2009.“ Data refer to the sole or principal job of full- and part-time workers, for wage and salary workers.
The gap between men’s and women’s full-time earnings narrowed slightly in 2009, according to new data from the Census Bureau’s American Community Survey.
For full-time, year-round workers, median earnings for women were 78.2 percent of men’s median earnings, or $35,549 compared with $45,485. In 2008, the ratio of women’s to men’s median earnings was 77.2 percent.

Women who worked full time in wage and salary jobs had median weekly earnings of $657 in 2009. This represented 80 percent of men's median weekly earnings ($819).